Acoustic Wave Therapy
Acoustic Wave Therapy, also known as shockwave therapy or radial wave therapy, uses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate healing and promote tissue regeneration.
What is Acoustic Wave Therapy?
Acoustic Wave Therapy is an application of shockwaves, which are pressure waves generated acoustically. In this therapy, focused shockwaves are directed at specific tissues of the body, such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bone, to achieve several effects.
Firstly, the shockwaves can break down tissue adhesions, bone spurs, or calcific deposits, facilitating their dissolution and removal. This controlled tissue disruption initiates a healing response in the body, prompting repair processes to commence in the treated area.
Additionally, the therapy stimulates the formation of new blood vessels, enhancing circulation to the treated tissue. This improved blood flow contributes to reduced pain and increased range of motion, promoting overall tissue healing and function.
In summary, acoustic wave therapy harnesses the power of focused shockwaves to target specific tissues, facilitating tissue repair, improving circulation, and alleviating pain and stiffness, without the need for invasive procedures or medications.

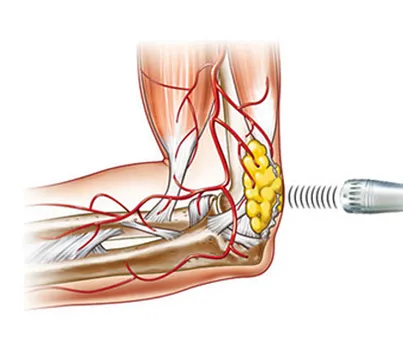
Help Your Body Heal Itself
Acoustic Wave Therapy, also known as shock wave therapy, triggers the body’s biological healing mechanisms by physically stimulating its cells. The response to this stimulus varies depending on the cell, resulting in various biological responses, including:
Reduction of Inflammation:
Wave therapy induces an anti-inflammatory effect through the sound waves it generates. These waves lower the production of inflammatory chemicals and regulate the immune response, effectively reducing inflammation. This is advantageous for conditions like tendinitis, bursitis, and arthritis.
Tissue Regeneration:
Wave therapy stimulates tissue regeneration by promoting the growth of new blood vessels, improving blood circulation, and enhancing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the affected area. This accelerates the healing process in conditions such as delayed bone healing, non-healing wounds, and ulcers.
Breakdown of Calcifications:
Wave therapy effectively breaks down calcifications or mineral deposits that form in soft tissues, such as tendons or muscles. This is especially beneficial for conditions like calcific tendinitis of the shoulder.
Pain Relief:
Dispersing the pain mediator “substance P,” shockwave therapy targets the neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting pain signals. By diminishing the concentration of substance P, this therapy effectively reduces the intensity and persistence of pain. The generated sound waves penetrate tissues, lowering substance P levels and providing relief from discomfort. Additionally, decreasing substance P can help alleviate inflammation and swelling, contributing to overall pain management and improved well-being.
Release of Trigger Points:
Trigger points are the primary cause of pain in areas like the back, neck, shoulders, and limbs, characterized by small lumps in tight muscle fibers. These trigger points contract intensely, cutting off their blood supply and leading to a buildup of waste products. This buildup irritates the nerves, causing further muscle contraction in a cycle known as “metabolic crisis.” Acoustic energy therapy helps reverse this crisis by releasing the trigger points, providing relief from pain.
Improved Mobility and Function:
Wave therapy can enhance joint mobility and functional outcomes by reducing pain, promoting tissue healing, and decreasing inflammation. This treatment aids patients in restoring range of motion, flexibility, and strength in the affected area, ultimately improving their overall quality of life.
Non-Invasive Alternative to Surgery
Wave therapy offers a non-invasive alternative for certain conditions that might otherwise necessitate surgical intervention. By adopting a conservative approach, it effectively manages pain and facilitates healing while sidestepping the potential risks and complications associated with surgery.


